A Learning Framework for Robust Bin Picking by Customized Grippers
Yongxiang Fan, Hsien-Chung Lin, Te Tang, Masayoshi Tomizuka
Welcome!
This page supplements our IROS2019 paper submission, in which we present a learning framework to plan robust grasps for bin picking with customized grippers. The framework contains an optimization-based planner by iterative surface fitting (ISF), and a learning-based explorer by regions with convolutional neural network (R-CNN).
Customized grippers have specifically designed fingers to increase the contact area with the workpieces and improve the grasp robustness. However, grasp planning for customized grippers is challenging due to the object variations, surface contacts and structural constraints of the grippers. In this paper, we propose a learning framework to plan robust grasps for customized grippers in real-time. The learning framework contains a low-level optimization-based planner to search for optimal grasps locally under object shape variations, and a high-level learning-based explorer to learn the grasp exploration based on previous grasp experience. The optimization-based planner uses an iterative surface fitting (ISF) to simultaneously search for optimal gripper transformation and finger displacement by minimizing the surface fitting error. The high-level learning-based explorer trains a regionbased convolutional neural network (R-CNN) to propose good optimization regions, which avoids ISF getting stuck in bad local optima and improves the collision avoidance performance. The proposed learning framework with RCNN-ISF is able to consider the structural constraints of the gripper, learn grasp exploration strategy from previous experience, and plan optimal grasps in clutter environment in real-time. The effectiveness of the algorithm is verified by experiments.
Paper Download
The full paper can be downloaded through this link.
Simulation Results on baseline-ISF
Video: Illustration of the grasp searching by baseline-ISF.
Experimental Results by baseline-ISF
Video: Bin picking task with the baseline-ISF. The method works fine in light clutter environment.
Experimental Results by RCNN-ISF
Light Clutter Environment
The R-CNN behaves similar with baseline initialization using K-means clustering in clean environment, as shown in below video.
Video: The experimental result by RCNN-ISF.
Heavy Clutter Environment
As the point cloud getting more complicated, the ISF initialization by K-means clustering becomes less-efficient.
Video: Inefficiency of the ISF search by K-means Cluttering. The K-means cluttering restricts the searching on discrete, isolated points, which is not sufficient to explore large point cloud.
In this paper, we utilize R-CNN to learn the good regions to initilize ISF search from previous grasping experience.
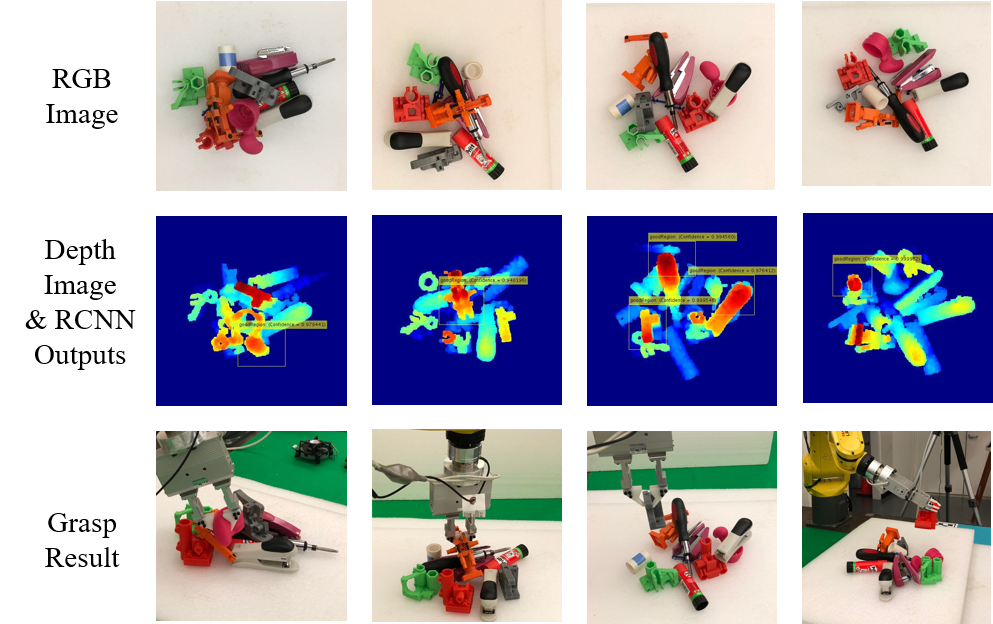 |
Fig: Grasp planning results on four clutter environments by RCNN-ISF. (Up) Clutter environment. (Middle) Selected regions by R-CNN to initialize ISF searching. (Bottom) Execution of the grasps planned by ISF.
Failure Mode
Point to plane fitting error may not be the best metric when choosing the optimal grasp from multiple feasible grasps.
Overall Summary Video
Contacts
contact my email for any questions: yongxiang_fanATberkeleyDOTedu